
How long would we hold out in the event of a Russian attack?".
^ " "Focșani Gate", the weak point of NATO's defense on the east flank. Radio Europa Liberă România (in Romanian). Cât de rapid oprește NATO o luptă cu Rusia?". ^ Popescu, Andrei Luca (21 October 2021). New Strategy Center, Centre for the Study of the New Generation Warfare. "The Focșani Gate – a key terrain for European security" (PDF). ^ a b c Mîndrescu, Mircea Melcher, Gregory Petersen, Phillip (2019). A possible Romanian invasion of Budjak for security purposes has been discussed by other analysts as well. It has been theorised that a Russian incursion into Ukraine's region of Budjak would put Romania's Focșani Gate and the Danube Delta at risk, which could force Romania to occupy the region. Such a scenario occurred on 24 February 2022. In early 2022, serious worries existed over whether or not Russia would invade Ukraine. It stands as a somewhat disconnected zone because of poor infrastructure, which makes it vulnerable to a potential attack from Russia. Today, the Focșani Gate is one of the most vulnerable strategic points in NATO of which Romania is now a member. Romania had already withdrawn from the Axis a few days before as a result of this offensive, subsequently being occupied by the Soviet Union and having a communist regime installed. Despite this, on 27 August 1944, the Red Army passed through the Focșani Gate and occupied the cities of Izmail, Galați and Focșani, allowing it to spread into the directions of Bucharest, the Black Sea and the Eastern Carpathians. 
It was heavily fortified by Nazi Germany-allied Romania during the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union (USSR). The Focșani Gate also played an important role in the Second Jassy–Kishinev offensive during World War II. Furthermore, important battles for Romania were fought in this area, including the defensive Battle of Mărășești and the offensive Battle of Mărăști, with the important defensive Third Battle of Oituz also having been fought near the Focșani Gate. As Romania faced defeat from the Central Powers, the Romanian Army retreated to the Focșani Gate.
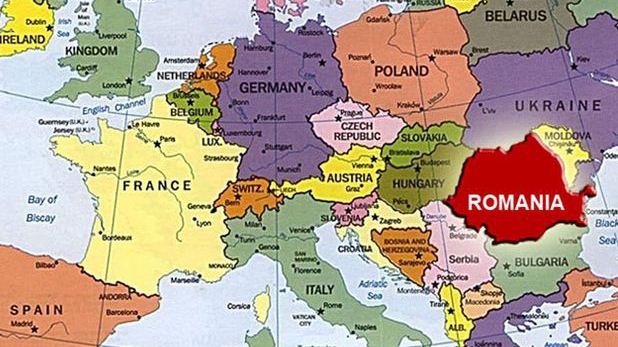
The Focșani Gate saw consideration in Hypothesis Z, Romania's war plan for World War I. To defend the Focșani Gate, the Focșani–Nămoloasa–Galați line was built. Concerns over Romania's defensive capabilities arose, and the studies were performed.

A few years before, Russia, a state then allied to Romania with which it had fought together in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878, had stripped away the region of Southern Bessarabia from Romania, causing tensions between the two countries. In that year, the government of Romania carried out a study to identify all the areas of the country where the terrain was not enough for defense and for engineering work to be taken on these areas to reinforce them. The area around the city of Focșani was already recognized as a weak point in Romania back in 1882.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
